Fluorinated Plastics Carry the Risk of Forever Chemicals: A Looming Threat to Public Health
Published on February 6, 2026 by Dr. Ahmad Mahmood
Introduction: When Durable Plastics Become a Public Health Hazard
Fluorinated plastics were designed to solve problems—heat resistance, chemical stability, and long product life. Yet those same properties have placed them at the center of a growing public health concern. Today, scientists warn that fluorinated plastics carry the risk of forever chemicals, substances that persist in the environment and accumulate in the human body.
Unlike many environmental threats that fade with time, fluorinated compounds linger for decades. Their durability has transformed them from industrial innovations into a looming threat to public health, affecting drinking water, food systems, and human biology on a global scale.
What Are Fluorinated Plastics?
Fluorinated plastics are polymers that contain fluorine atoms bonded to carbon. The most well-known examples include PTFE, PVDF, and other fluoropolymers commonly used in industrial, medical, and consumer products.
Why Fluorine Is Added to Plastics
Fluorine-carbon bonds are among the strongest in organic chemistry. This gives fluorinated plastics:
- Resistance to heat and corrosion
- Non-stick and water-repellent properties
- Long service life under extreme conditions
These qualities made fluorinated plastics indispensable in aerospace, electronics, cookware, packaging, and infrastructure.
Understanding “Forever Chemicals” (PFAS)



Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large family of chemicals closely linked to fluorinated plastics. Many PFAS are used directly in plastic production or form as byproducts.
Why PFAS Do Not Break Down
PFAS are often called “forever chemicals” because their molecular structure resists natural degradation. Sunlight, bacteria, and water—forces that normally break down pollutants—have little effect on them. As a result, PFAS accumulate in:
- Soil
- Rivers and groundwater
- Wildlife
- Human blood and organs
According to research referenced by the Environmental Protection Agency, PFAS have now been detected in a majority of tested water systems worldwide.
How Fluorinated Plastics Release PFAS
Manufacturing, Use, and Disposal Pathways
PFAS contamination does not come from a single source. It occurs throughout the plastic lifecycle:
- Manufacturing: Emissions and wastewater from fluoropolymer production
- Use: Wear, heating, or friction releases microscopic particles
- Disposal: Landfills and incineration allow PFAS to leach or spread
Even products marketed as “stable” can shed PFAS over time, especially under heat or mechanical stress.
Where Fluorinated Plastics Are Found in Daily Life
Fluorinated plastics are far more common than most people realize. They are found in:
- Non-stick cookware coatings
- Food packaging and grease-resistant papers
- Medical devices and protective equipment
- Electronics and wire insulation
- Industrial seals, membranes, and pipes
Because exposure comes from many small sources, total PFAS intake is often cumulative rather than obvious.
Human Health Risks Linked to PFAS Exposure

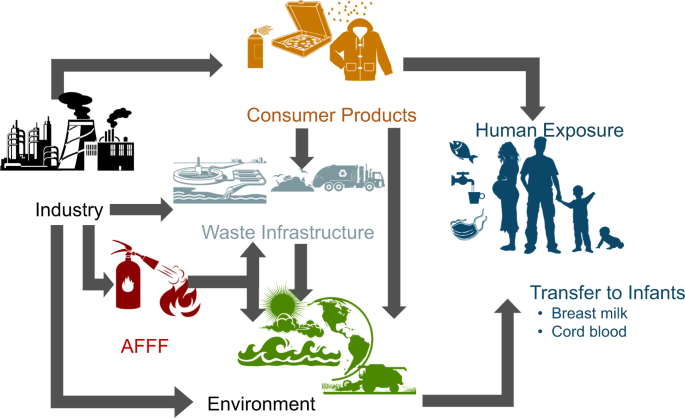
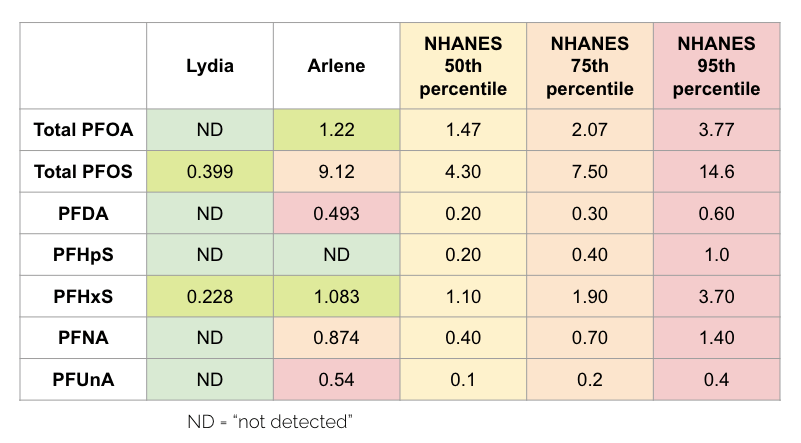
Scientific evidence increasingly links PFAS exposure to a wide range of health concerns.
Long-Term and Cumulative Health Effects
Peer-reviewed studies summarized by the World Health Organization suggest associations between PFAS and:
- Hormonal and endocrine disruption
- Immune system suppression
- Elevated cholesterol levels
- Reproductive and developmental effects
- Increased risk of certain cancers
What makes PFAS particularly dangerous is bioaccumulation. Even low-level exposure can become harmful over time as these chemicals remain in the body for years.
Environmental Persistence and Global Spread
Once released, PFAS travel easily through water and air. They have been detected in:
- Arctic ice
- Remote mountain lakes
- Marine ecosystems
- Agricultural soils
This global distribution demonstrates that fluorinated plastics are not just a local pollution issue—they are a planetary one.
Why Current Regulations Lag Behind the Science
Regulation has struggled to keep pace with PFAS research. Thousands of PFAS compounds exist, yet only a small fraction are regulated individually. This chemical-by-chemical approach leaves major gaps.
International bodies like the United Nations Environment Programme increasingly advocate for regulating PFAS as a class rather than one compound at a time—a shift many scientists say is overdue.
Economic and Social Costs of PFAS Contamination
The financial burden of PFAS pollution is enormous. Communities face:
- Expensive water treatment upgrades
- Healthcare costs linked to chronic exposure
- Property value declines
- Long-term environmental remediation
These costs often fall disproportionately on low-income and rural communities, raising serious environmental justice concerns.
Safer Alternatives and Emerging Solutions
Innovation is beginning to challenge fluorinated plastics dominance. Alternatives include:
- Non-fluorinated barrier coatings
- Mechanical rather than chemical non-stick surfaces
- Reusable and refill-based product systems
- Green chemistry approaches to polymer design
While no single solution fits all uses, many applications no longer require fluorinated materials.
What Governments, Industries, and Individuals Can Do
Meaningful change requires action at every level:
- Governments: Class-based PFAS regulation and transparency
- Industries: Phase-out non-essential fluorinated plastics
- Individuals: Reduce reliance on non-stick and disposable products
Public awareness has already accelerated policy discussions worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are all fluorinated plastics dangerous?
Not all pose equal risk, but many are linked to PFAS release over time.
2. Can PFAS be removed from the body?
They leave the body very slowly; prevention is the most effective strategy.
3. Are PFAS found in drinking water?
Yes, they have been detected in many water systems globally.
4. Why are they still used if they are harmful?
Their durability and performance delayed recognition of long-term risks.
5. Are alternatives available?
Yes, safer materials are increasingly viable for many uses.
6. What makes this a public health issue?
Widespread exposure, persistence, and links to chronic disease.
Conclusion: Why the Fluorinated Plastics Debate Is a Public Health Turning Point
Fluorinated plastics carry the risk of forever chemicals not because they were poorly designed—but because they were designed to last forever in a world that cannot safely absorb them. As evidence mounts, the conversation is shifting from convenience to consequence.
Addressing this looming threat to public health will define how societies balance innovation, safety, and sustainability in the decades ahead.