Environmental Impact of AI Energy Water and Climate Effects
Published on March 1, 2026 by Dr. Ahmad Mahmood
The environmental impact of AI is growing as artificial intelligence systems expand across industries. Training large models, running data centers, and powering digital infrastructure require significant energy and water resources. As a result, AI development now intersects directly with climate policy and environmental management.
While AI offers efficiency gains in transportation, energy optimization, and research, it also increases electricity demand. Therefore, understanding the environmental impact of AI is essential for responsible innovation.
What Drives the Environmental Impact of AI
The environmental impact of AI comes primarily from three sources:
• Electricity consumption
• Water use for cooling
• Hardware manufacturing
Training advanced machine learning models requires massive computing power. Data centers run continuously to process queries, store data, and deliver real time results.
Consequently, global electricity demand from data infrastructure continues to rise.



Caption: AI systems rely on energy intensive data centers that require constant electricity and cooling.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions
The environmental impact of AI depends heavily on the energy source powering data centers. If facilities rely on fossil fuels, emissions increase. However, if renewable energy supplies the grid, carbon intensity decreases.
In the United States, electricity generation varies by region. Some states rely heavily on natural gas, while others integrate wind, solar, or hydropower.
Therefore, the climate footprint of AI is location dependent.
At the same time, rising digital demand adds pressure to grid stability. You can explore broader grid challenges in our analysis of renewable energy transition.
Water Use and Cooling Demands
Beyond electricity, the environmental impact of AI includes water consumption. Data centers require cooling systems to prevent overheating. Many facilities use evaporative cooling that consumes large volumes of water.
In drought prone regions, this creates tension between digital growth and water security.
Moreover, climate change intensifies heat waves, which increases cooling demand. As temperatures rise, water consumption for cooling may also rise.
Water stress already affects many regions. You can see related risks in our coverage of global water risk.
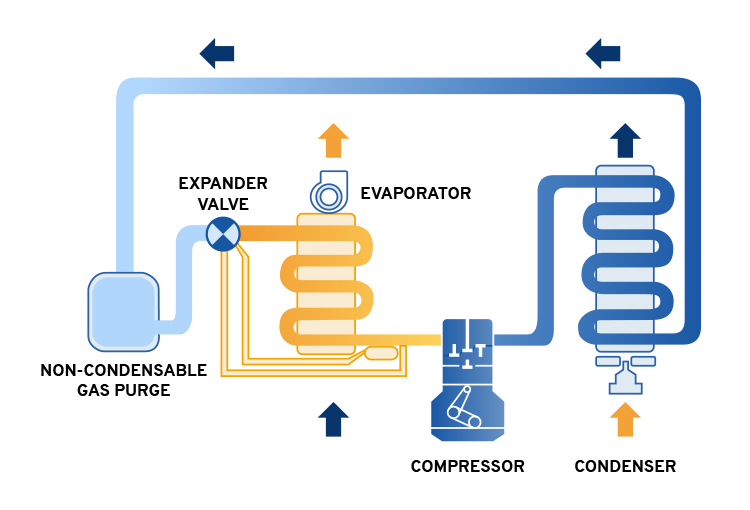
Caption: Cooling systems link digital infrastructure growth to regional water availability.
Hardware Manufacturing and Resource Extraction
The environmental impact of AI also extends to hardware production. Advanced chips require rare earth elements, lithium, cobalt, and other minerals.
Mining and processing these materials generate land disturbance, water pollution, and carbon emissions.
In addition, rapid hardware upgrades increase electronic waste. Discarded servers and devices contribute to growing e waste streams worldwide.
This issue connects to broader concerns about resource extraction and circular economy strategies. You can explore systemic resource management in our discussion of circular economy principles.
Can AI Reduce Its Own Environmental Impact
Although AI consumes energy, it can also optimize systems. For example, AI tools improve:
• Smart grid management
• Energy efficiency in buildings
• Supply chain logistics
• Climate modeling accuracy
Therefore, the environmental impact of AI is not purely negative. The net effect depends on policy, energy sources, and system design.
If companies power data centers with renewable energy and improve hardware efficiency, environmental pressure decreases.
However, without oversight, rapid expansion may outpace efficiency gains.
Regulation and Corporate Accountability
Governments increasingly examine the environmental impact of AI infrastructure. Policymakers now consider reporting requirements, energy transparency, and grid integration planning.
At the corporate level, technology firms publish sustainability reports to address investor concerns.
Transparency matters. As digital infrastructure grows, public scrutiny increases.
Responsible AI development must include environmental metrics, not just performance benchmarks.
The Future of AI and Environmental Sustainability
The environmental impact of AI will likely expand as adoption accelerates. However, the direction of that impact remains flexible.
If energy grids decarbonize and cooling systems become more efficient, AI could operate within sustainable limits. Conversely, if fossil fuel dependence persists, emissions may rise sharply.
Therefore, policymakers, engineers, and business leaders must align digital innovation with climate goals.
AI is not separate from environmental systems. It depends on electricity, water, minerals, and land. Understanding these dependencies helps societies balance technological progress with ecological stability.
The environmental impact of AI ultimately reflects broader infrastructure decisions.