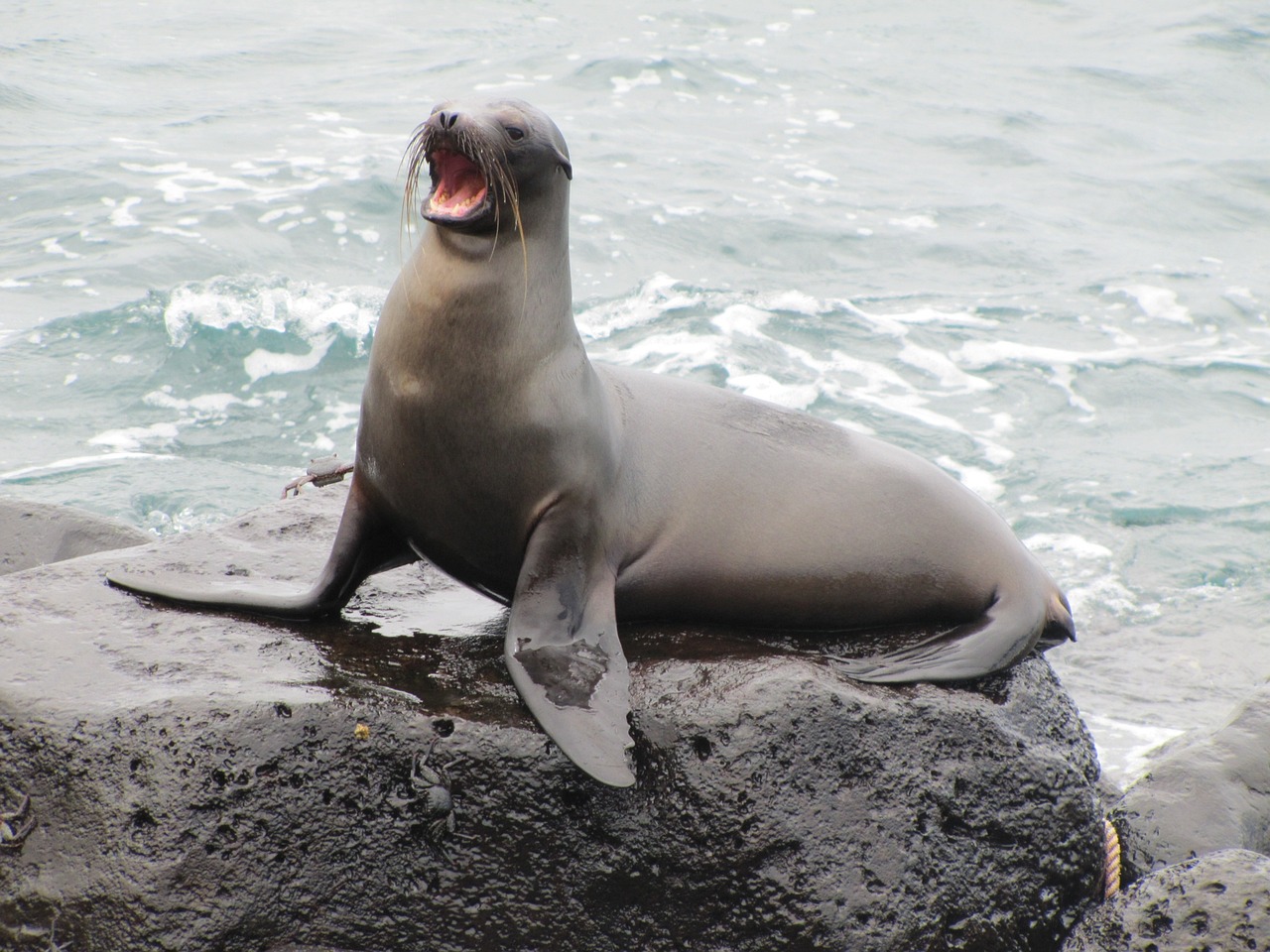
The increase in cases of bird flu in sea lions along the Pacific coast has raised concerns about the health of these marine mammals and the environment they live in. The virus, which is highly contagious among birds, can be fatal to sea lions and other marine mammals if left untreated. In this article, we will discuss the impact of bird flu on sea lions and the environment and what can be done to prevent the spread of the virus.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Bird Flu?
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects birds. The virus is capable of causing severe disease and even death in birds and can be transmitted from bird to bird through contact with infected saliva, nasal secretions, or feces. In recent years, there have been several outbreaks of bird flu in sea lions along the Pacific coast, causing concern among marine biologists and animal welfare organizations.
How does Bird Flu affect Sea Lions?
Sea lions are highly susceptible to bird flu and can easily contract the virus if they come into contact with infected birds or their droppings. The virus can cause severe respiratory illness in sea lions and can lead to death if left untreated. In addition to the direct impact on sea lions, bird flu can also have indirect effects on their health by compromising their immune systems, making them more susceptible to other diseases.

The Impact of Bird Flu on the Environment
In addition to the direct impact on sea lions, bird flu can also have indirect effects on the environment. The virus can spread rapidly among birds, killing large numbers of birds and altering the balance of ecosystems. This can lead to a decline in the overall health of the environment, as well as a reduction in the number of birds available to perform important ecological functions such as pollination and seed dispersal.
Preventing the Spread of Bird Flu
To prevent the spread of bird flu, it is important to take steps to reduce the risk of transmission from birds to sea lions. This can be done by avoiding direct contact with infected birds and their droppings, and by ensuring that any sick birds are promptly isolated and treated. In addition, it is important to monitor sea lion populations for signs of bird flu and to take prompt action if an outbreak is detected. This may involve the use of antiviral medications, supportive care, and other measures to prevent the spread of the virus and minimize its impact on sea lions and the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bird flu is a serious threat to the health of sea lions and the environment. However, by taking steps to prevent the spread of the virus and promptly treating infected animals, it is possible to minimize its impact and ensure the long-term health of these important marine mammals and their ecosystems.
FAQs
- Can bird flu be transmitted from sea lions to humans? No, bird flu is not known to be transmitted from sea lions to humans. The virus is primarily transmitted from birds to other birds, and while sea lions can contract the virus if they come into contact with infected birds or their droppings, they are not believed to be a significant source of transmission to humans.
- What are the symptoms of bird flu in sea lions? The symptoms of bird flu in sea lions can include respiratory distress, coughing, and nasal discharge. In severe cases, the virus can lead to pneumonia and other serious health problems, and may result in death if left untreated.
- Can bird flu be treated in sea lions? Yes, bird flu can be treated in sea lions with antiviral medications and supportive care. However, prompt treatment is important to minimize the impact of the virus and ensure the best possible outcome for the affected animal.







2 thoughts on “Bird Flu in Sea Lions and Environmental Degradation”
Pingback: Is the Bird Flu the Next Pandemic? - Sustainability Awakening
Pingback: Protecting Our Canine Companions from Canine Influenza