Table of Contents
ToggleSection 1: Introduction to Renewable Energy
Harnessing nature’s bounty:
As humanity grapples with the rising tide of climate change, our need for clean and sustainable energy has never been more pressing. Thankfully, nestled within the very fabric of our planet lies a treasure trove of renewable resources, waiting to be harnessed. Let’s embark on a captivating journey into the intricate world of renewables energy, where nature’s boundless bounty empowers our lives without jeopardizing the planet’s well-being..
Sustainable solutions:
The sun beams down, painting the sky with gold. A gentle breeze whispers through the leaves, carrying the scent of rain. These seemingly mundane elements hold the key to a brighter future, a future powered by nature’s bounty through the magic of renewable energy. But what makes renewables not just an alternative, but a sustainable solution? Buckle up, for we’re about to dive into the heart of sustainability, where energy and future generations meet in a vibrant dance of possibility.
Principle 1: Meeting Present Needs without Compromising the Future
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and leave behind a trail of environmental destruction, renewables draw on inexhaustible resources – the sun, wind, water, and the Earth’s heat. Imagine solar panels harvesting sunlight without depleting a drop of oil, or wind turbines generating electricity without spewing pollutants into the air. This is the core of sustainability – meeting our energy needs today without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to do the same.
Principle 2: Addressing Resource Depletion
Fossil fuels are a one-time use resource, their dwindling reserves fueling anxieties about energy security. Renewables, however, offer a limitless wellspring of power. The sun will continue to shine, the wind will continue to blow, and the Earth’s core will continue to simmer, ensuring a perpetual source of energy for generations to come. This not only eliminates the dependence on finite resources but also fosters energy independence, empowering nations and communities to chart their own sustainable paths.
Principle 3: Combating Pollution and Climate Change
The dark clouds of pollution cast a shadow over our planet, a grim consequence of our reliance on fossil fuels. Renewables, however, come bathed in the light of environmental responsibility. Solar panels produce no emissions, wind turbines leave the air clean, and geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat without adding to the atmospheric burden. This shift towards clean energy is crucial in the fight against climate change, allowing us to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the devastating effects of global warming.
Renewables in Action: Addressing Pressing Issues
The benefits of renewables go beyond mere principles. Let’s see how they tackle the most pressing issues of our time:
Resource Depletion: Imagine wind farms dotting landscapes previously ravaged by oil rigs, their turbines spinning with the promise of a future free from resource scarcity.
Pollution: Picture bustling cities powered by rooftop solar panels, their skies clear and blue, devoid of the smog that once choked their lungs.
Climate Change: Envision vast oceans dotted with offshore wind farms, their blades churning not just electricity but hope, hope for a world where rising sea levels and scorching heatwaves become a fading memory.
The Road Ahead: Embracing a Sustainable Future
The journey towards a sustainable future powered by renewables is not without its bumps. Technological advancements, infrastructure development, and policy changes are all crucial pieces in the puzzle. Yet, with unwavering commitment and collaborative efforts, we can overcome these challenges. Imagine a world where energy is not a privilege for the few, but a right for all, a world where renewable resources fuel not just our homes, but also our ambitions, a world where future generations inherit a legacy of clean air, vibrant ecosystems, and boundless energy.
Combating climate change:
The specter of climate change looms large, casting a long shadow over our future. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and melting glaciers – these are not distant nightmares, but the harsh realities brought on by our reliance on fossil fuels. But even in the face of this daunting challenge, hope flickers bright in the form of renewable energy. This potent weapon in our arsenal holds the key to mitigating climate change and building a future bathed in sustainability.
Fossil Fuels: The Culprits Behind the Warming Tide
For over a century, we’ve fueled our progress with fossil fuels – coal, oil, and natural gas. These convenient energy sources, however, come at a hefty price. When burned, they release greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. These invisible blankets trap heat, causing the planet’s temperature to rise – a phenomenon known as global warming.

Section 2: Types of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources
Solar Power:
However, instead of just a tan, you’re generating electricity! .That’s the magic of solar power. Photovoltaic cells, like microscopic factories, capture sunlight and transform it directly into electricity. Rooftop panels turn homes into miniature power plants, and vast solar farms illuminate entire cities. Also solar isn’t just about electricity. Solar thermal collectors concentrate the sun’s heat, powering water heaters, desalination plants, and even industrial processes. The cost of solar has plummeted, making it increasingly accessible and even competitive with traditional options. The sun shines free, and with solar power, we can tap into its boundless potential.
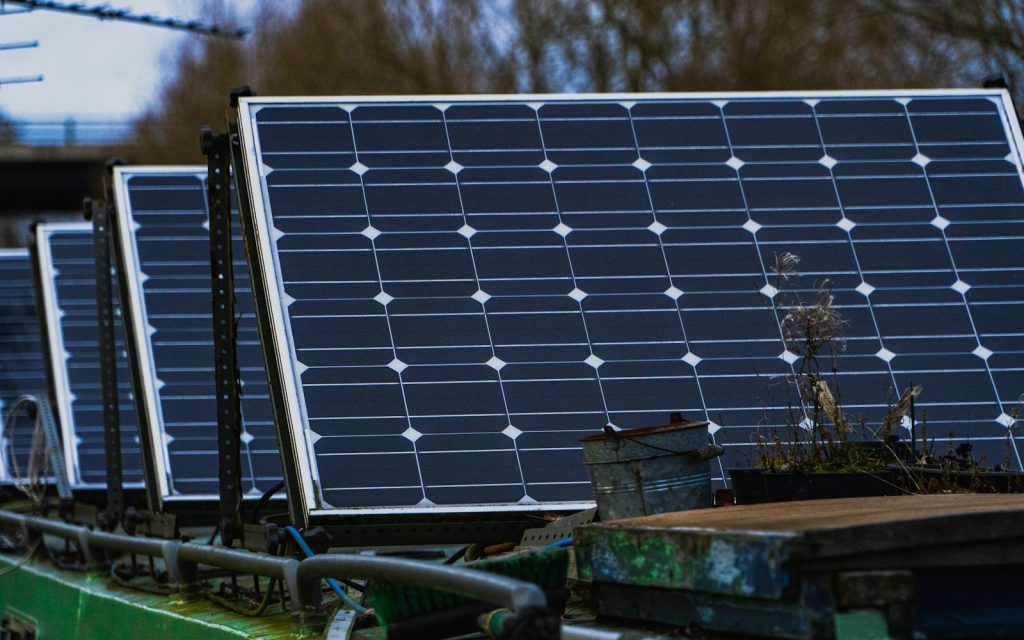

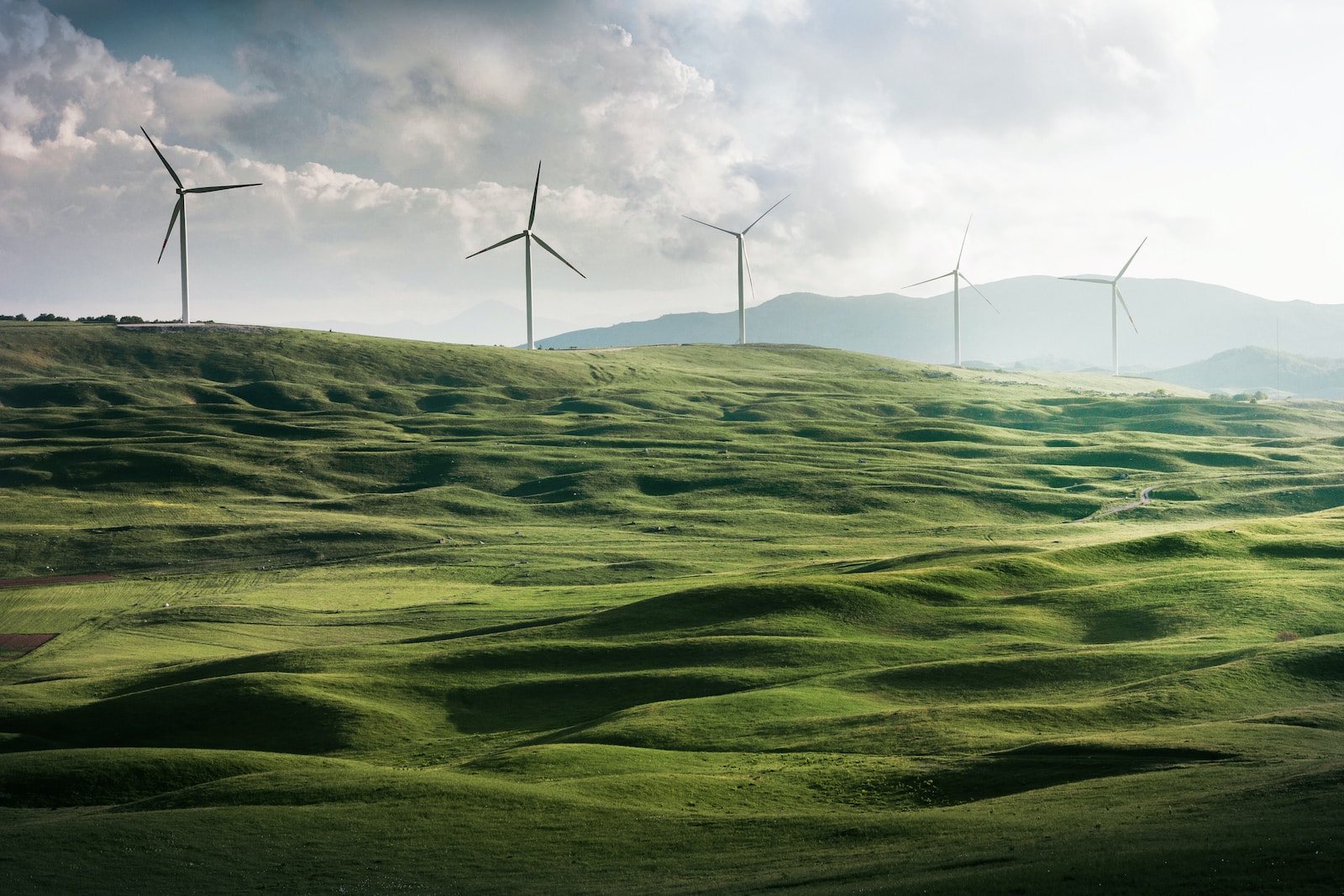
Wind Power:
Once relegated to windmills in fields, wind energy has morphed into a technological marvel. Towering turbines, their blades slicing through the air, capture the wind’s kinetic energy and transform it into electricity. Onshore wind farms dot landscapes, while offshore turbines, like sentinels of the sea, harness the ocean’s powerful breezes. Different turbine designs cater to varied wind speeds and terrain, maximizing efficiency. Technological advancements have brought down costs and boosted output, making wind a cost-effective and reliable renewable source. Witness the majestic dance of these modern windmills, and feel the promise of clean energy whispering on the breeze.
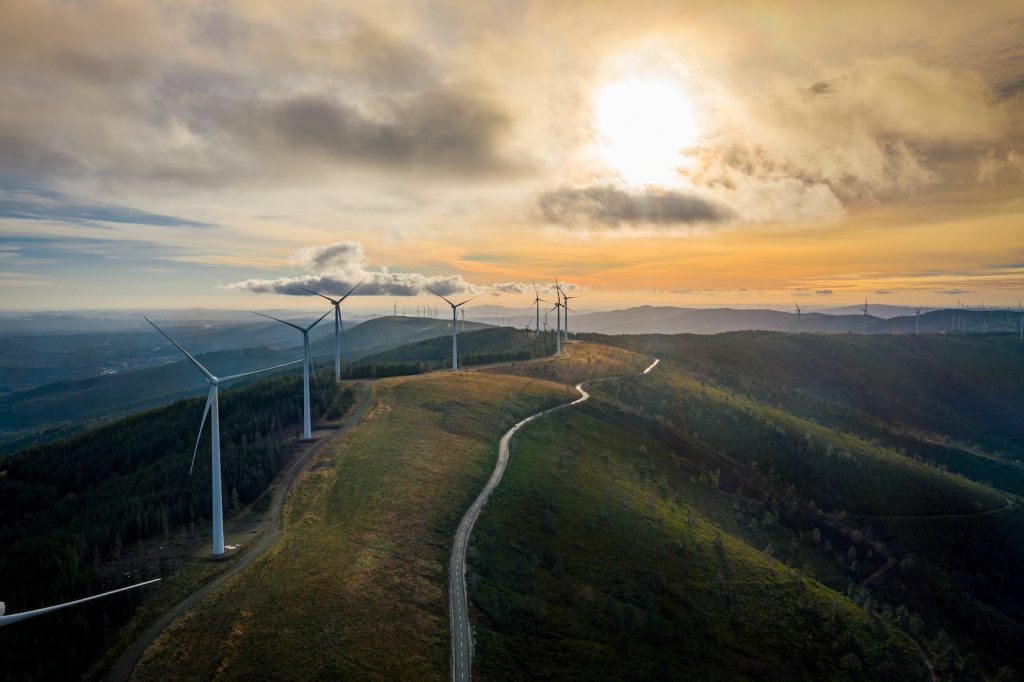

Hydropower:
Hydropower, a veteran of the renewable energy scene, utilizes the power of falling water. Dams built on rivers channel water through turbines, generating electricity. It’s a mature technology, providing a significant and reliable chunk of the world’s renewable energy. From the iconic Hoover Dam to smaller run-of-the-river projects, hydropower continues to play a crucial role. While concerns about environmental impact exist, advancements in smaller-scale and fish-friendly technologies strive to minimize the footprint of this long-standing renewable source.
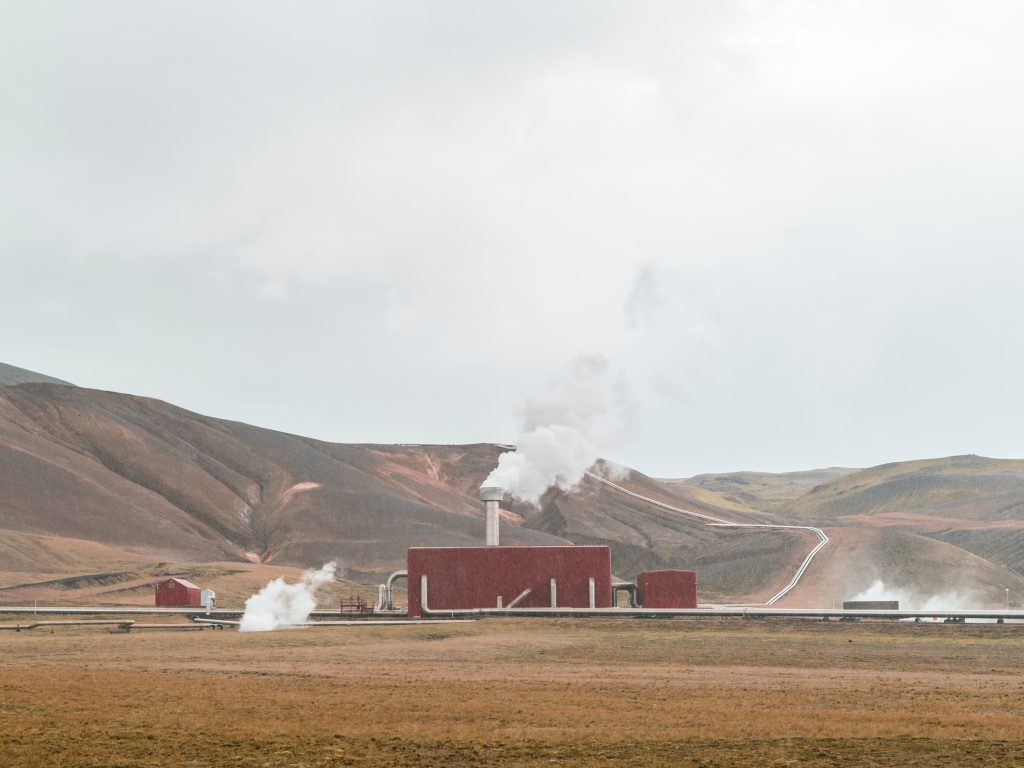
Geothermal Energy:
Beneath our feet lies a fiery cauldron, heating the Earth’s core. Geothermal energy utilizes this hidden heat, accessed through wells that extract hot water and steam. The steam drives turbines to generate electricity, while the hot water can directly heat homes and buildings. Iceland, with its volcanic activity, is a geothermal haven, but resources exist worldwide, waiting to be tapped. Technological advancements allow us to access deeper and less obvious geothermal pockets, expanding the potential of this clean and reliable energy source.

Biomass Energy:
Plants, wood residues, even agricultural waste – biomass encompasses a diverse range of organic matter, all holding a hidden energy potential. Biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted into biofuels for transportation. Gasification and anaerobic digestion further expand its potential, generating electricity and biogas. Biomass presents both challenges and opportunities. Balancing its use with sustainable practices like reforestation is crucial. But when managed responsibly, biomass offers a versatile renewable resource, returning energy to the Earth from whence it came.

Ocean Energy:
The ocean, vast and powerful, hides an untapped energy treasure trove. Tides rise and fall, waves crash against the shore, and currents surge beneath the surface – all these hold the potential for electricity generation. Tidal turbines, mimicking their wind counterparts, harness the ebb and flow of tides. Wave energy converters extract the power of surging waves, while ocean thermal energy conversion utilizes the temperature difference between deep and surface ocean waters. While still in its nascent stages, ocean energy holds immense promise, offering a glimpse into a future where the ocean becomes a significant contributor to our energy mix.
Section 3: Advantages of Renewable Energy
Environmental benefits:
Fossil fuels leave a trail of environmental destruction – greenhouse gas emissions warming the planet, air pollution choking our lungs, water contamination poisoning ecosystems, and land degradation scarring landscapes. But renewables paint a different picture, singing a symphony of environmental harmony:
Greenhouse Gas Reductions: Every kilowatt-hour of renewable energy generated is a blow against climate change. Studies show significant reductions in carbon dioxide emissions with widespread adoption of renewables, mitigating the effects of global warming and protecting Earth’s future.
Cleaner Air: Renewables breathe new life into our skies. They don’t emit harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, leading to cleaner air, healthier lungs, and reduced respiratory illnesses.
Healthy Ecosystems: Renewables protect our precious water resources, minimizing the risk of contamination from spills and accidents associated with fossil fuel extraction and transportation. This safeguards crucial ecosystems and biodiversity.
Sustainable Land Use: Unlike fossil fuel exploration and extraction, which can scar landscapes and disrupt habitats, renewables like solar and wind farms require minimal land use. This allows for sustainable land management and preserves crucial ecological balances.
Energy independence:
Beyond environmental benefits, renewables empower nations and communities through energy independence:
Reduced Reliance on Imports: Shifting to renewables frees countries from dependence on foreign oil and gas, reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations and political instability. This fosters greater energy security and resilience.
Diversification of Energy Sources: Renewables offer a diverse menu of energy sources, reducing reliance on any single, potentially volatile, resource. This promotes flexibility and adaptability in the face of changing markets and geopolitical landscapes.
Domestic Energy Production: Renewables unlock the potential for local energy production, creating jobs and boosting the economy within communities. This empowers regions and reduces vulnerability to external factors.
Job creation:
The transition to renewables isn’t just about saving the planet – it’s about creating a cleaner, more vibrant economy:
New Jobs Across Sectors: Renewables drive job creation in diverse sectors, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance, research and development, and project management. This fosters economic growth and empowers communities.
Skilled Workforce Development: Renewables demand a skilled workforce, leading to investments in education and training programs. This empowers individuals and creates a more competitive and innovative economy.
Green Collar Jobs for a Sustainable Future: Renewables offer the opportunity for individuals to be part of the solution to climate change, contributing to a cleaner future while pursuing rewarding careers.
Technological advancements:
The world of renewables is constantly evolving, with cutting-edge advancements powering the future:
Higher Efficiency Solar Panels: Bifacial panels capture sunlight from both sides, boosting efficiency and output. This maximizes land use and minimizes the footprint of solar farms.
Advanced Wind Turbine Designs: Longer blades capture more wind energy, while lighter materials increase efficiency and reduce costs. This makes wind power more accessible and competitive.
Micro-Hydro and Run-of-the-River: Smaller hydropower solutions harness the power of smaller rivers and streams, minimizing environmental impact and offering localized renewable energy options.
Long-term affordability:
While upfront costs of some renewable technologies may seem high, the long-term picture is one of sustainable affordability:
Stable and Predictable Costs: Unlike volatile fossil fuel prices, renewables offer stability and predictability. Costs are declining with technological advancements and economies of scale, making them increasingly competitive.
Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Lower reliance on fossil fuels means less exposure to price fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties. This translates to long-term cost savings and stability.
Investing in the Future: Renewables represent an investment in a clean and sustainable future. The benefits for health, environment, and economic well-being far outweigh the initial costs.
Section 4: Is Nuclear Energy Renewable?

Unpacking the debate:
Nuclear energy, often dubbed the “clean giant” of the energy world, remains a controversial topic. While undeniably producing power without greenhouse gas emissions, its status as a “renewable” source and its inherent risks spark heated debate. Let’s delve into the complexities of this potent energy source, examining both its advantages and limitations.
On the Bright Side: Clean Powerhouse
- Carbon-Free Champion: Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear power plants don’t emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases during operation. This makes them a significant contributor to mitigating climate change and tackling global warming.
- Reliable Powerhouse: Nuclear power boasts remarkably high capacity factors, generating electricity consistently year-round, unaffected by weather conditions like wind or sunlight. This ensures a stable and dependable energy supply.
- Energy Dense, Space Efficient: Compared to other energy sources, nuclear power packs a tremendous punch in a small footprint. A single plant can generate electricity for millions of homes, requiring minimal land usage compared to solar or wind farms.
But Shadows Linger: Limitations and Concerns
- Nuclear Waste Conundrum: Radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants poses a long-term disposal challenge. While solutions like deep geological repositories exist, concerns about long-term safety and potential environmental impact persist.
- Accident Fears: While rare, the potential for serious accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima casts a long shadow over nuclear power. Addressing public safety concerns and implementing stringent safety measures remain crucial for widespread acceptance.
- Limited Renewability: Unlike truly renewable sources like solar or wind, nuclear fuel resources are finite, even though uranium reserves are still substantial. This raises concerns about long-term sustainability and dependence on non-renewable resources.
Finding the Nuance: Towards a Balanced Future
The debate surrounding nuclear energy is not black and white. Its contribution to clean energy production is undeniable, yet the challenges associated with waste disposal, safety, and resource limitations demand careful consideration. Finding a balanced approach necessitates:
- Investing in Research and Development: Continued research on advanced reactor designs, fuel recycling technologies, and safer waste disposal solutions is crucial to mitigate risks and improve the overall sustainability of nuclear power.
- Transparency and Public Engagement: Open communication about safety measures, risk assessments, and waste management plans is essential to build public trust and acceptance of nuclear energy.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Relying solely on any single energy source, including nuclear, carries inherent risks. Building a diverse energy mix that incorporates renewables, nuclear, and energy efficiency measures fosters a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
- Limited resources:
While nuclear energy boasts clean power generation, its dependence on uranium, a finite resource, raises concerns about long-term sustainability. Current estimates suggest uranium reserves could last centuries, but depletion anxieties persist. Exploring alternative fuel sources like thorium and investing in fuel recycling technologies to maximize resource utilization are crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of nuclear power.
- Safety considerations:
Address public concerns about potential nuclear accidents and the long-term safety of nuclear waste disposal. Discuss safety measures employed in modern nuclear plants and advancements in waste management technologies.
Section 5: Myths and Misconceptions about Renewable Energy
Busting the myths:
Renewables often encounter a barrage of misconceptions, casting shadows on their tremendous potential. Let’s shed some light on four common myths and reveal the facts powering their rise:
Myth #1: Unreliable Sun, Fickle Wind:
While solar and wind power depend on weather, advancements in forecasting and grid interconnection significantly improve their reliability. Modern grids can source from diverse renewable and traditional sources, ensuring consistent supply. Germany, for instance, sources over 25% of its electricity from solar power, showing effective integration.
Myth #2: Green but Expensive:
Costs of renewables are plummeting. Solar panel costs have dropped by over 90% since 2010, making them cost-competitive with fossil fuels in many regions. Wind energy too shows similar cost reductions. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that over two-thirds of new renewable power installations are cheaper than the cheapest existing coal option.
Myth #3: Can’t Power Us All:
Renewables are rapidly scaling up. In 2022, renewable energy capacity additions outpaced all other sources globally. Countries like Iceland and Costa Rica run almost entirely on renewables, proving their ability to meet entire energy demands. With continued investments and advancements, renewables can power our future.
Myth #4: Sun Sets, Lights Out:
Intermittency challenges exist, but solutions are at hand. Grid modernization allows smarter integration of renewables, while energy storage technologies like pumped hydro and advanced batteries store excess generation for use during peak demand. Smart grid management systems further optimize energy distribution and ensure grid stability.
Intermittency challenges:
Acknowledging that solar and wind have periods of lower generation, let’s explore how we can overcome these hurdles:
Grid Modernization: Upgrading grids with smart technologies allows for better forecasting, demand response, and integration of diverse energy sources.
Energy Storage Solutions: Advancements in battery technology offer grid-scale storage options, while pumped hydro provides long-duration storage. Other innovative solutions like thermal storage and hydrogen production are also emerging.
Regional Cooperation: Interconnecting grids across regions with diverse weather patterns allows for sharing and balancing of renewable energy resources.
Grid integration and storage:
Seamless integration of renewables into existing grids requires:
Standardized protocols and infrastructure: This facilitates efficient connection and communication between renewable energy sources and the grid.
Energy storage deployment: Strategic placement of storage facilities near generation or high-demand areas optimizes their utility.
Policy and regulatory frameworks: Supportive policies and regulations encourage investments in grid modernization and storage technologies.
Section 6: Renewables Energy in the Business Sector
Greening corporations:
The winds of change are blowing through the corporate landscape, carrying the scent of sustainability and powered by renewable energy. Businesses are rapidly realizing that going green isn’t just a feel-good PR move – it’s a sound business decision. Let’s explore how corporations are harnessing the power of renewables to gain a competitive edge and build a brighter future for themselves and the planet.

Going Green, Gaining Green: The Competitive Edge of Renewables
Cost Savings: Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuels. Businesses investing in on-site solar panels or signing power purchase agreements with renewable energy generators can see significant reductions in their electricity bills.
Enhanced Brand Image: Consumers are increasingly eco-conscious, and choosing businesses that prioritize sustainability resonates with them. Embracing renewables strengthens a company’s brand image, attracting and retaining customers who value environmental responsibility.
Future-Proofing Operations: Fossil fuels are finite and subject to volatile price fluctuations. By investing in renewables, businesses lock in stable energy costs and mitigate the risks associated with fossil fuel dependence.
Attracting and Retaining Talent: Top talent seeks purpose and values alignment. Companies committed to sustainability attract and retain skilled employees who want to work for an organization that shares their environmental values.
Renewable energy procurement:
The path to renewable energy is diverse, offering choices to suit every business:
On-site Generation: Installing solar panels or wind turbines on company property allows for direct generation and consumption of clean energy.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Businesses can enter into contracts with renewable energy developers to purchase electricity generated from projects like solar farms or wind farms.
Community Solar Gardens: Joining a community solar garden allows businesses to share the benefits of a nearby solar installation without needing rooftop space.
The business case for renewables:
The economic benefits of renewables for businesses are compelling:
Reduced Electricity Bills: Studies show that businesses can save 10-30% on their electricity costs by switching to renewable energy.
Tax Incentives and Government Subsidies: Many governments offer financial incentives like tax breaks, rebates, and feed-in tariffs to encourage businesses to adopt renewables.
Increased Property Value: Buildings with on-site renewable energy generation often command higher property values due to lower operating costs and enhanced marketability.
Improved Employee Morale and Productivity: Employees working for companies committed to sustainability experience higher morale and engagement, leading to improved productivity and performance.
Section 7: The Future of Renewable Energy
Technological breakthroughs:
Smart Grids Orchestrating the Symphony:
Intelligent grids are emerging, utilizing advanced sensors, data analytics, and machine learning to optimize energy flows, integrate disparate renewable sources, and prioritize sustainable choices. Imagine a grid anticipating demand fluctuations, seamlessly routing surplus solar power to homes when the sun sets, and dynamically adjusting to weather patterns.
Blockchain:
Democratizing Power with Transparency: Blockchain technology, the bedrock of cryptocurrencies, is finding its way into energy markets. Decentralized, secure platforms promise peer-to-peer energy trading, empowering individuals and communities to sell excess solar power directly to neighbors, fostering a collaborative and transparent energy future.
AI Optimizing the Dance of Supply and Demand:
Artificial intelligence is poised to become the maestro of renewable energy production and storage. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, predict weather patterns, optimize generation schedules, and manage storage to ensure seamless integration of renewables into the grid, maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
Beyond Wind and Sun:
New Kids on the Renewable Block: The renewable energy playground is expanding! Imagine algae biofuels cultivated in vast ponds, powering vehicles with their photosynthetic prowess. Or harnessing the micro-currents of rivers and streams with miniature hydropower turbines, generating clean energy in remote locations. The possibilities are endless.
Global energy transformation:
Fast forward to 2050, and witness a global energy mix where renewables reign supreme. Studies predict their share surpassing 50%, with wind and solar leading the charge, complemented by a diverse mosaic of geothermal, hydropower, and emerging technologies. This not only ensures a sustainable future for the planet but also unlocks an avalanche of opportunities.
Green Jobs Sprouting Across the Globe:
Millions of new green jobs will bloom across the globe, from manufacturing and installing cutting-edge renewable technologies to managing smart grids and developing advanced biofuels. This green jobs revolution will empower communities, revitalize economies, and offer fulfilling careers for generations to come.
A sustainable future:
Imagine vibrant communities nestled amongst solar farms and wind turbines, their rooftops adorned with panels harvesting the sun’s bounty. Electric vehicles glide silently on smart roads, powered by clean energy coursing through a decentralized grid. Sustainable practices become integral to daily life, from responsible waste management to energy-efficient homes.
Section 8: How to Transition to Renewable Energy
Go Green at Home:

Choose renewable energy providers for your electricity.
Harness the sun with rooftop solar panels.
Swap out appliances for energy-efficient models.
Reduce consumption with smart habits and unplug unused electronics.
Join the Community Force:
Invest in co-operative solar projects or community energy gardens.
Advocate for pro-renewable policies through local campaigns and awareness programs.
Share your green journey and inspire others to join the movement.
Amplify the Collective Voice:
Support organizations pushing for clean energy policies.
Hold corporations accountable for their environmental footprint.
Invest in sustainable businesses and technologies.
Be part of the global movement demanding a just transition to renewables..
Section 9: Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future
At the crossroads of energy and environment, a critical choice beckons. We stand with one foot rooted in the familiar, fossil-fueled past, its shadow stretching long across our planet’s health. And with the other, we take a tentative step towards a sun-drenched future, paved with the boundless potential of renewable energy.
Nuclear energy, often shrouded in controversy, sits at a curious intersection. Its ability to generate clean, baseload power undeniably contributes to reducing carbon emissions. Yet, the specter of accidents, waste disposal issues, and resource limitations linger, casting doubt on its sustainability credentials. While nuclear energy may play a role in the transitional phase, its future seems inextricably linked to advancements in safety, waste management, and fuel reprocessing.
But it is renewable energy that truly ignites the imagination. Picture vast fields bathed in golden sunlight, their photovoltaic cells humming with the silent music of captured photons. Imagine towering turbines slicing through the wind, their blades spinning a symphony of clean electricity. Envision the Earth’s very heat, pulled from its geothermal depths, warming homes and powering industries. This is the future renewables offer, a future where energy flows not from dwindling reserves, but from the inexhaustible bounty of nature.
The transition to renewables won’t be easy. Challenges like grid integration, intermittency, and storage solutions demand innovative minds and unwavering commitment. Yet, the economic, environmental, and social benefits are undeniable. Renewable energy promises cleaner air, reduced dependence on fossil fuels, and a thriving green economy brimming with new jobs and technological advancements.
call to action
echoes across continents. Individuals can make a difference by switching to renewable energy providers, embracing energy-efficient practices, and advocating for supportive policies. Businesses can join the revolution by investing in renewable projects, setting ambitious sustainability goals, and inspiring responsible consumer choices. Governments must play their part by implementing supportive policies, investing in research and development, and ensuring a just transition for workers in the fossil fuel industry.
This is not merely a technological shift; it’s a cultural transformation. It’s about embracing a new relationship with our planet, recognizing its inherent bounty, and harnessing its renewable resources with respect and responsibility. It’s about building a future where clean air is a birthright, not a privilege, and where energy empowers, not pollutes.
In the face of climate change’s looming shadow, embracing renewables is not just a choice; it’s an imperative. Let us rise to meet this challenge with the same spirit of innovation and collaboration that has defined our past. Let us leave behind a legacy not of fossil fuels and fumes, but of sun-kissed fields, wind-kissed hills, and the enduring promise of a brighter future powered by renewables.
So, let the sun be our guide, the wind our song, and the Earth’s boundless energy our fuel. Together, let us power a revolution, not just in energy, but in our very relationship with the planet. For in the embrace of renewables lies not just a cleaner future, but a future worthy of generations to come.