Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
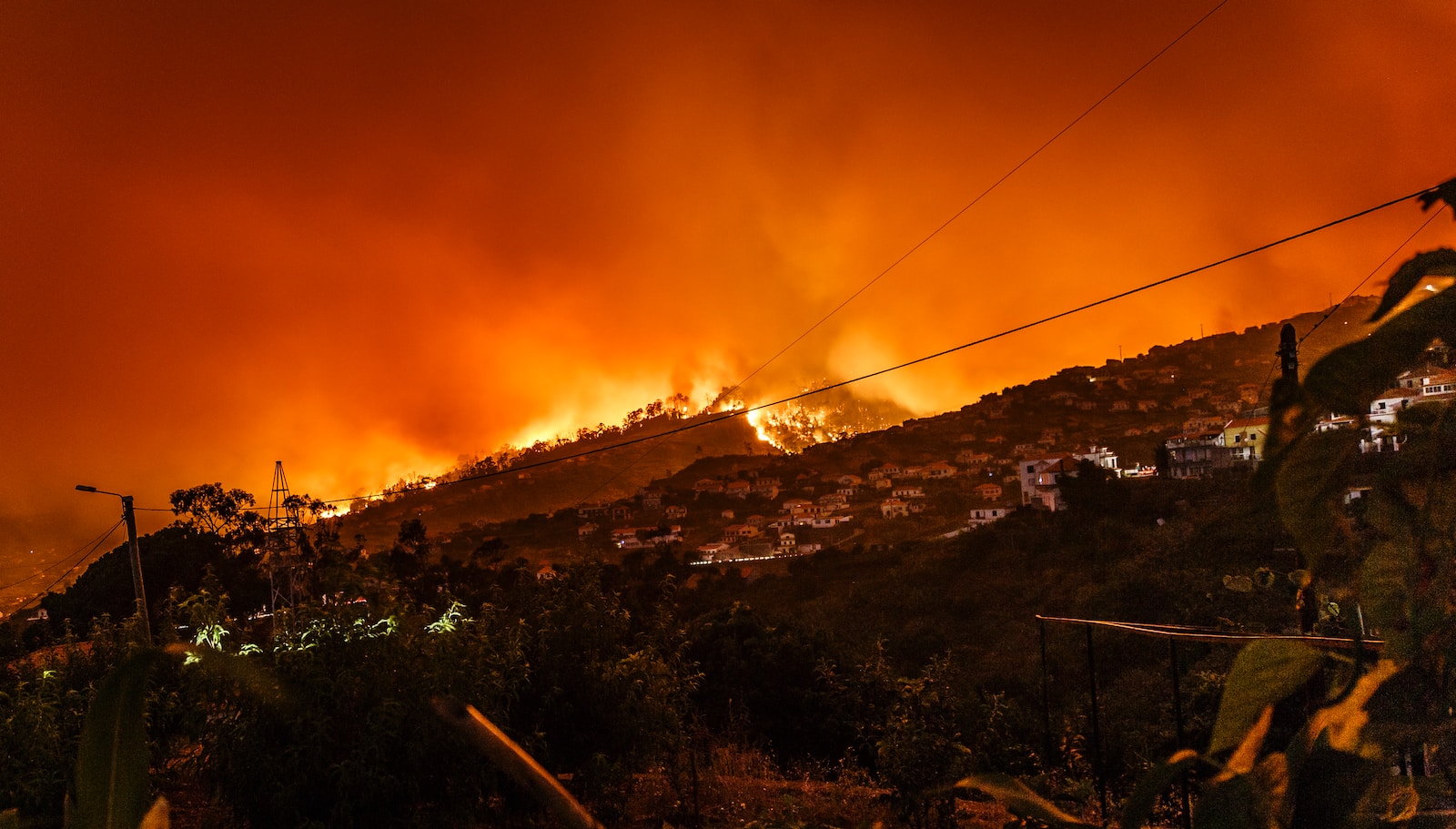
Climate change has become a significant catalyst for the increasing occurrence of fast-spreading wildfires, as highlighted in a recent Californian study. The findings shed light on the rising dangers associated with wildfires, offering valuable lessons in prevention and mitigation, particularly in the wake of recent devastating disasters in Canada, Greece, and Hawaii.
Understanding the Link Between Climate Change and Extreme Wildfires
Scientists at the Breakthrough Institute, a non-profit research center, conducted an extensive study published in the journal Nature. Using machine learning techniques, they analyzed the relationship between higher average temperatures, drier conditions, and the frequency of “extreme” wildfires. The study revealed a 25% increase in such wildfires compared to the pre-industrial era, attributing it to human-caused warming.
Analyzing the Risk of Extreme Wildfires
To assess the risk, researchers examined a series of wildfires that occurred from 2003 to 2020. By utilizing computer models and considering variables such as precipitation, wind, and absolute humidity, they measured the probability of a given fire evolving into an “extreme” one. The study also warned that changes in these variables could exacerbate the risks posed by global warming.
The Varied Impact of Climate Change on Wildfires
The impact of climate change on wildfires varied depending on the conditions. In some partially dry areas, global warming pushed the region beyond critical thresholds, significantly increasing the likelihood of extreme fires. However, in extremely dry conditions, the influence of climate change was comparatively less pronounced. Lead author Patrick Brown emphasized the importance of focusing on places and times historically on the moist side of these thresholds but pushed onto the dry side due to background warming.
Projected Increase in Wildfire Risk by the End of the Century
The study’s calculations revealed alarming projections for future wildfire risks. Under a “low-emissions” scenario, limiting global warming to 1.8 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, the average risk could increase by 59% by the end of the century. In an uncontrolled, high-emissions scenario, the risk could surge by up to 172%. With Earth’s surface already having warmed 1.2°C, urgent action is necessary to mitigate these potential outcomes.
Lessons from Recent Wildfire Disasters
The publication of this study follows a series of devastating wildfires in California, 2020 being a particularly fierce year. The state witnessed numerous fatalities, with over four million acres consumed by flames. Similarly, Hawaii and Canada experienced significant wildfires that resulted in loss of life and displacement of residents. These events underscore the need for comprehensive understanding and effective prevention measures.
Prevention Measures: Using Insights to Combat Wildfires
The study’s findings offer crucial insights into dryness thresholds, which can aid in the implementation of prevention measures. Thinning and prescribed burning of vegetation in strategic locations can reduce the amount of dry fuel, mitigating the risks wildfires pose. Hazardous fuel reduction, when conducted at scale, has the potential to offset the impact of climate change, resulting in a future with reduced wildfire danger.
Importance of Awareness and Risk Mitigation
Experts emphasize the increasing importance of awareness and risk mitigation efforts. The study’s insights can guide precautions regarding power lines, inform targeted monitoring and awareness campaigns, and assist in deploying firefighting resources effectively. Authorities and individuals must recognize the elevated fire risks and take necessary measures to protect lives, property, and the environment.
Rebalancing Expenditure for Effective Wildfire Prevention
In a separate briefing by wildfire specialists, it was highlighted that expenditure on wildfires typically leans heavily toward response and recovery efforts, rather than prevention and mitigation measures. It is crucial to rebalance expenditure by allocating more resources to proactive measures such as managing vegetation and fire-danger forecasting. A global shift toward improved risk mitigation strategies is necessary to combat the growing menace of wildfires.
As extreme wildfires become 25% more frequent due to climate change, it is imperative to understand the implications, implement preventive measures, and rebalance expenditures accordingly. By prioritizing awareness, risk mitigation, and effective prevention strategies, we can strive for a future with reduced wildfire danger despite climate change. Together, we can combat the escalating threat of wildfires and protect our communities and natural resources.